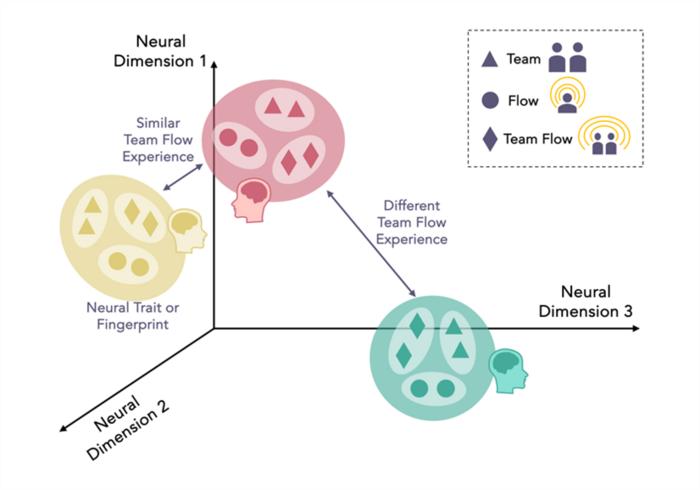
 Using AI To Find Neural Traits In Social Interaction
Using AI To Find Neural Traits In Social InteractionAn algorithm that maps individual brain activity can reveal a “neural fingerprint” of ...
 Prosthetic Hearing: Soft Brainstem Implant One Step Closer To Human Trials
Prosthetic Hearing: Soft Brainstem Implant One Step Closer To Human TrialsThe cochlear implant has helped many regain hearing functionality and a new study shows a potential...
 Duckweed Science May Lead To Food That Farms Itself
Duckweed Science May Lead To Food That Farms ItselfDuckweed split into different species 59 million years ago, when the climate was more extreme than...
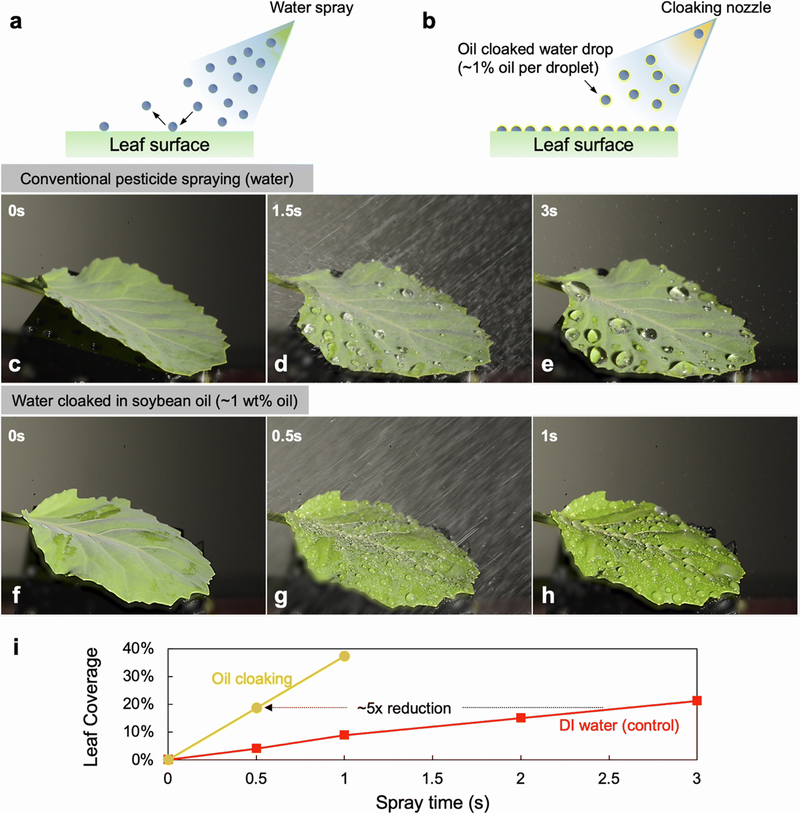 Sticky Pesticides Reduce Chemicals Needed To Protect Plants
Sticky Pesticides Reduce Chemicals Needed To Protect PlantsIt's easy for Greenpeace employees in cities to talk about farming but in the real world, without...