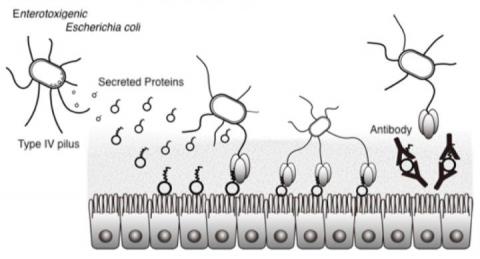
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is a major cause of diarrhea in developing countries, and responsible for at least 300,000 deaths a year, according to the World Health Organization.
Effective vaccines have not been developed, so patients infected are treated with antibiotics and supporting measures. The emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria has become a concern so the development of new treatment methods is ongoing.
Blood thinning drugs are preventing 7,000 strokes each year, according to an analysis of general practice records of five million patients from 2000 to 2016 to find out how many people have a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and how many are receiving treatment to prevent strokes.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cause of an irregular heartbeat and five times increases the risk of stroke. To reduce the risk of stroke by around two thirds, patients with atrial fibrillation are given anticoagulant drugs to prevent blood clotting, such as warfarin.
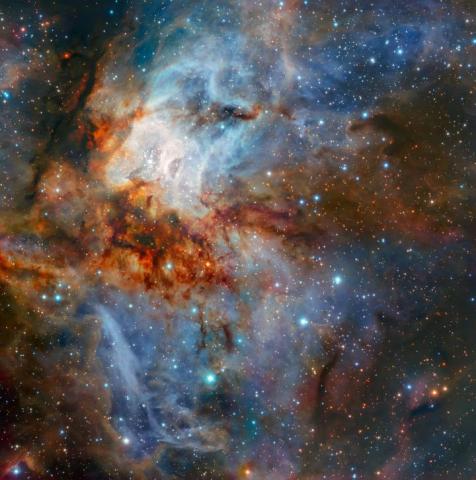
By using infrared wavelengths, the HAWK-I infrared imager mounted on ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile was able to capture this image of the star cluster RCW 38.
RCW 38 is over 5,00 light years away (look toward the constellation Vela) and is composed of several short-lived massive stars that will eventually supernovae, but also has some 8,000 other x-ray emitting objects.
In Ely, about 250 north of Las Vegas, Nevada is scheduled to hold its first execution in 12 years.
Nothing controversial about that, because in 2002 Scott Dozier murdered Jeremiah Miller after he traveled to Las Vegas where Dozier had promised to help him make methamphetamine. Dozier dumped him in a trash bin, three years later killed at least one other person, and has been on "death row" since 2007. And nothing controversial about Dozier wanting to die rather than spend the rest of his life in prison.
Genetic testing has been overcome by companies selling hype. Even 23andMe, arguably the most prominent,
was chastised by FDA for promising peace of mind when they couldn't do anything of the kind.
What about actual research involving the testing of human biospecimens? Should individual research results on a study-specific basis be done through an informed decision-making process? If so, how? And when?
Seabirds love fish and fishing nets are a ready source of food. Peru's gillnet fleet comprises the largest component of that nation's small-scale fleet and is conservatively estimated to set 100,000 kilometers of net per year in which thousands of turtles and seabirds die as "bycatch" or unintentionally.
Five years ago, California set out to be a world leader in adopting ambitious greenhouse gas reduction targets and created the world's fourth-largest carbon-trading program. Not bad for one state.
Except it isn't helping the state, it is subsidizing others. And some of the emissions targets are not emissions at all, they are instead epidemiological claims like small micron particulate matter (PM2.5), which have had zero acute deaths but were the target of EPA and California environmentalists despite a lack of evidence.
Life may be common amongst the stars, but perhaps very far away. But new research published in
Nature hints that it could be much closer than we expected. And it may be on a world of water and ice.
It seems that in a posthumous gift to humanity, the celebrated
Cassini spacecraft may have revealed that Enceladus, one of saturn's great moons,
holds the building blocks of life.
Worldwide poverty has dropped dramatically, we are in the Long Peace when it comes to war, the old cycles of famine boom and bust have leveled off, science has made it possible for everyone to live better for longer and spend less on basic necessities.
The world continues to improve. Why, then, do polls consistently show that people believe otherwise? The answer may lie in a phenomenon called "prevalence induced concept change."
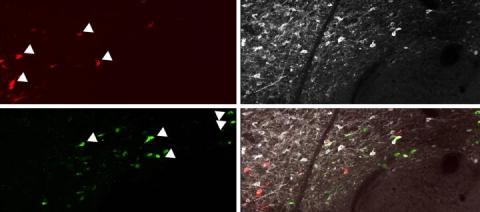
Fear is a healthy response, kept intact over eons of evolution, but sometimes it can be irrational. A new brain circuit discovery may help make sense of the madness.
The study details the role of dopamine in ensuring that rats stop being afraid when there isn't anything to be afraid of anymore.