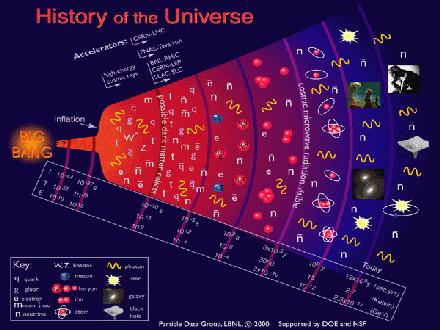
A mechanistic common cause for inflation and dark energy using only standard model physics
A mechanistic common cause for inflation and dark energy using only standard model physicsRather than providing another functional construct to fit observational cosmology, a mechanistic...
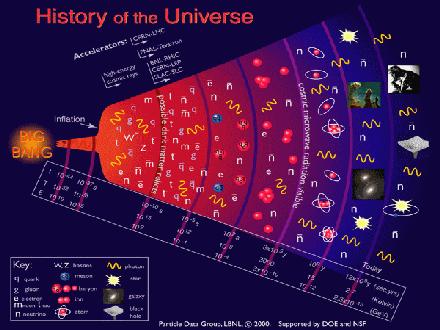 There Is Still Hope After Entropy
There Is Still Hope After EntropyThe first law of thermodynamics is commonly known as the law of conservation of energy. This...
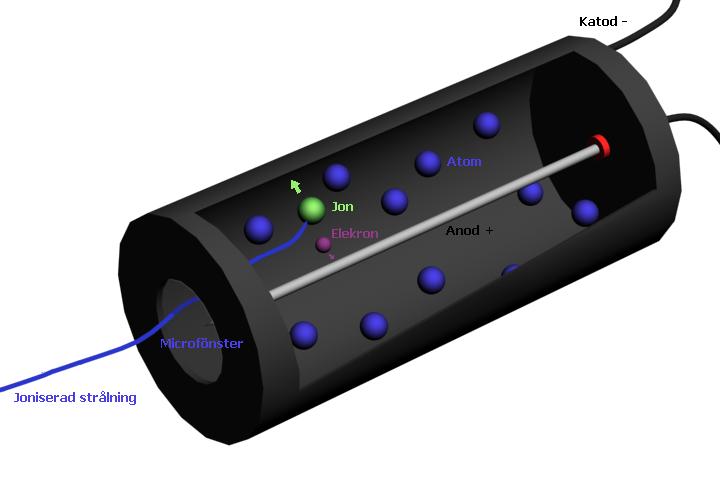
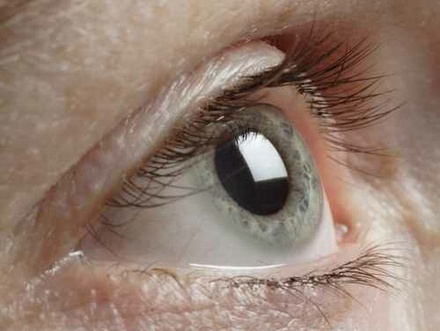 Your Eyes As Radiation Detectors
Your Eyes As Radiation Detectors When you look at the rainbow, what you see is the prism like effect of the mist (aerosolized water...
 Archeology Can Reveal Truth
Archeology Can Reveal TruthThe modern definition of science could be stated that it is a systematic study of the natural...