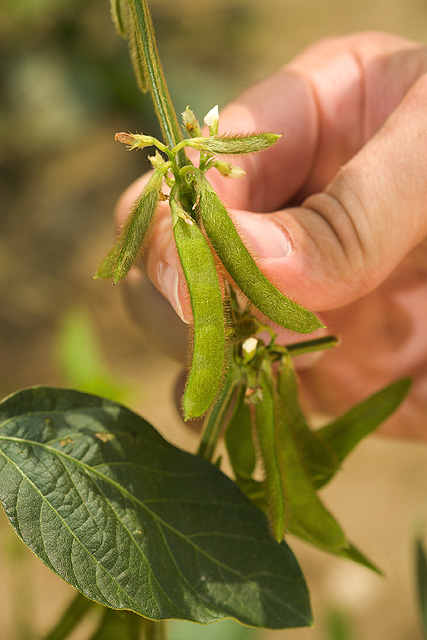
Smarter Soybeans Mean Affordable Food In Poorer Regions
Smarter Soybeans Mean Affordable Food In Poorer RegionsIt is easy for wealthy countries to spend $135 billion on an organic food process that uses higher...
 Shorter Course Of Post-Mastectomy Radiation With Breast Reconstruction Is Safe And Effective
Shorter Course Of Post-Mastectomy Radiation With Breast Reconstruction Is Safe And EffectiveA multi-institutional study has found that a shorter course of post-mastectomy radiation, combined...
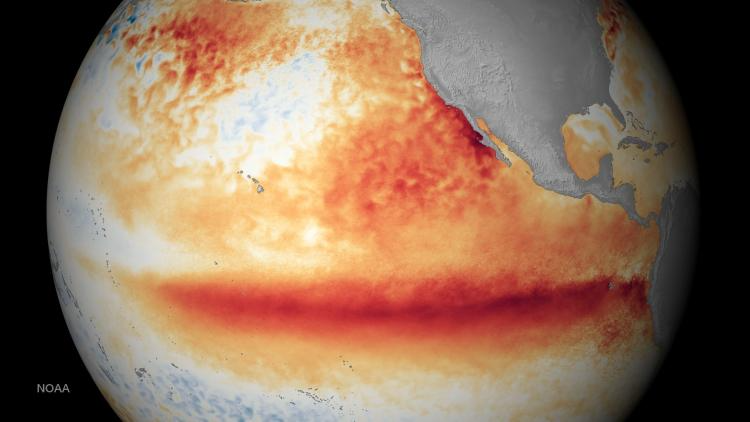 Simulation Predicts 50% Of Recurring El Niño Events Could Be Extreme In 25 Years
Simulation Predicts 50% Of Recurring El Niño Events Could Be Extreme In 25 YearsThe recurring El Niño phenomenon was in full force from mid-2023 to mid-2024 and as predicted...
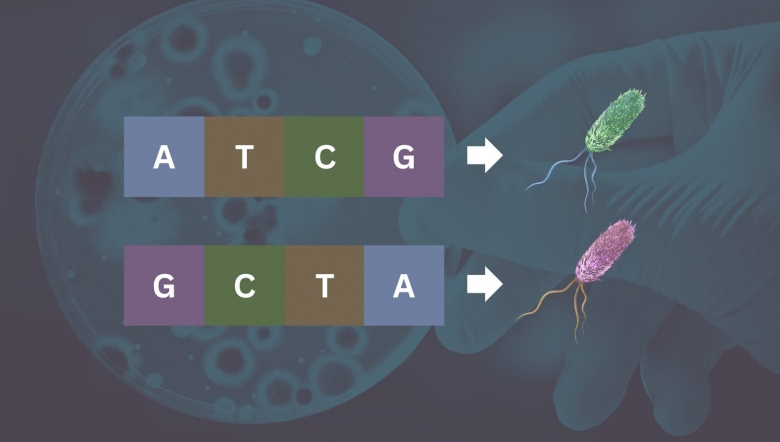 Bacterial Genes Can Be Genetic Shapeshifters
Bacterial Genes Can Be Genetic ShapeshiftersProkaryotes, single-cell organisms such as bacteria, undergo inversions which cause a physical...