Is your personality set in stone at a young age? If you were a jerk in high school will you still be a jerk at 60? Not necessarily. And what changes there are may not be defining. The only time you might see a big disparity could be when comparing yourself to others.
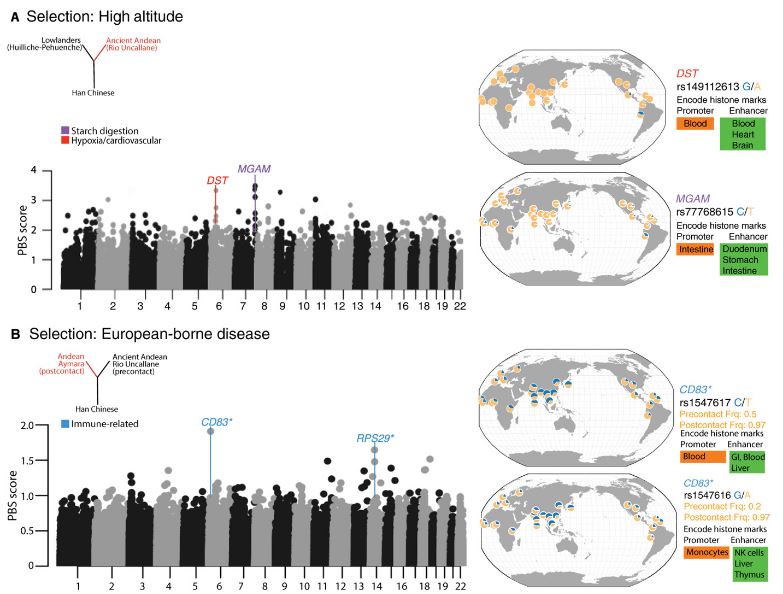
Recent DNA analyses show that ancient populations in the Peruvian highlands adapted wild tubers into potatoes - and then those potatoes in turn modified them in ways distinct from other global populations.
Potatoes are native to South America and became an agricultural crop in the Andean highlands of what is now Peru. But wild tubers genetically modified into potatoes did something interesting in return; they altered the genomes of the Andeans who made it a staple of their diet. Co-evolution. This co-evolution between agriculture and human is evident in the configuration of a gene associated with starch digestion in the small intestine - MGAM - in the agricultural ancient Andean genome samples, but not in hunter-gatherers down the coast.
In 2016, a Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) vaccine candidate named the RSV F Vaccine failed in Phase III trials, which could have been a crippling blow for Novavax, but they may be on the road to recovery.
Companies have to have Phase III trials before they can get approval. Phase I proves safety and dosing while Phase II shows it is better than a placebo and Phase III is intended to show it either works better than existing treatments or has fewer side effects. That's all after numerical models and animal studies. Since FDA essentially doubled the costs to get drug approval in the early 2000s only the most promising drug advances to Phase III. perhaps 1 in 5,000 that look good on a computer. It simply isn't worth the cost otherwise.
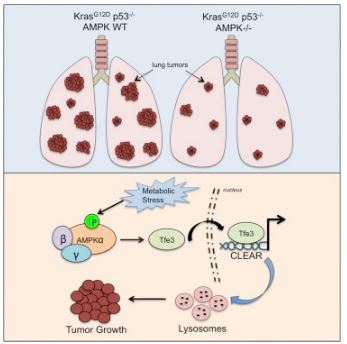
The protein complex AMPK is thought to suppress cancer, by slowing cellular metabolism, but it can also help some tumors grow.
But why? A new study says it has solved the mystery.
AMPK acts as a fuel gauge for the cell, overseeing energy input and output to keep the cell running smoothly. Similar to a car sensor flashing a low-gas signal or turning off a vehicle’s AC to save energy, AMPK slows down cell growth and changes the cell’s metabolism if the cell’s fuel (nutrients) is low.
The Great Pyramids have long been held up as the pinnacle of ancient engineering. Over 100 structures, some as high as were constructed of huge alabaster blocks, many quarried from Hatnub - the site of an new interesting discovery.
Given the challenges in building such huge structures, it is no surprised the Great Pyramid of Khufu is one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It and others were built thanks to quarries connected to the Nile by Bronze Age roads. The blocks were transported by sleds. But what about construction? Huge ramps? Were they poured? Some even speculated about aliens.
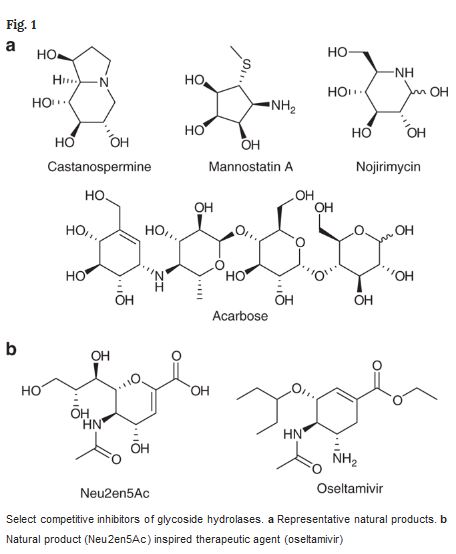
New molecules similar to carbohydrates have showed the capacity to inhibit the activity of a specific type of glycoside enzymes - and that means inhibiting infectious diseases.
Glycosides are essential enzymes to digest carbohydrates but they are also key players in infections caused by pathogens, in anti-bacterial defense and many other vital cellular processes. Because these small molecules that are able to bond with and inhibit the activity of enzymes in infectious diseases, it opens up the basis for new medicines.
 What Next For Messenger RNA (mRNA)? Maybe Inhalable Vaccines
What Next For Messenger RNA (mRNA)? Maybe Inhalable Vaccines Toward A Single Dose Smallpox And Mpox Vaccine With No Side Effects
Toward A Single Dose Smallpox And Mpox Vaccine With No Side Effects ChatGPT Is Cheaper In Medicine And Does Better Diagnoses Even Than Doctors Using ChatGPT
ChatGPT Is Cheaper In Medicine And Does Better Diagnoses Even Than Doctors Using ChatGPT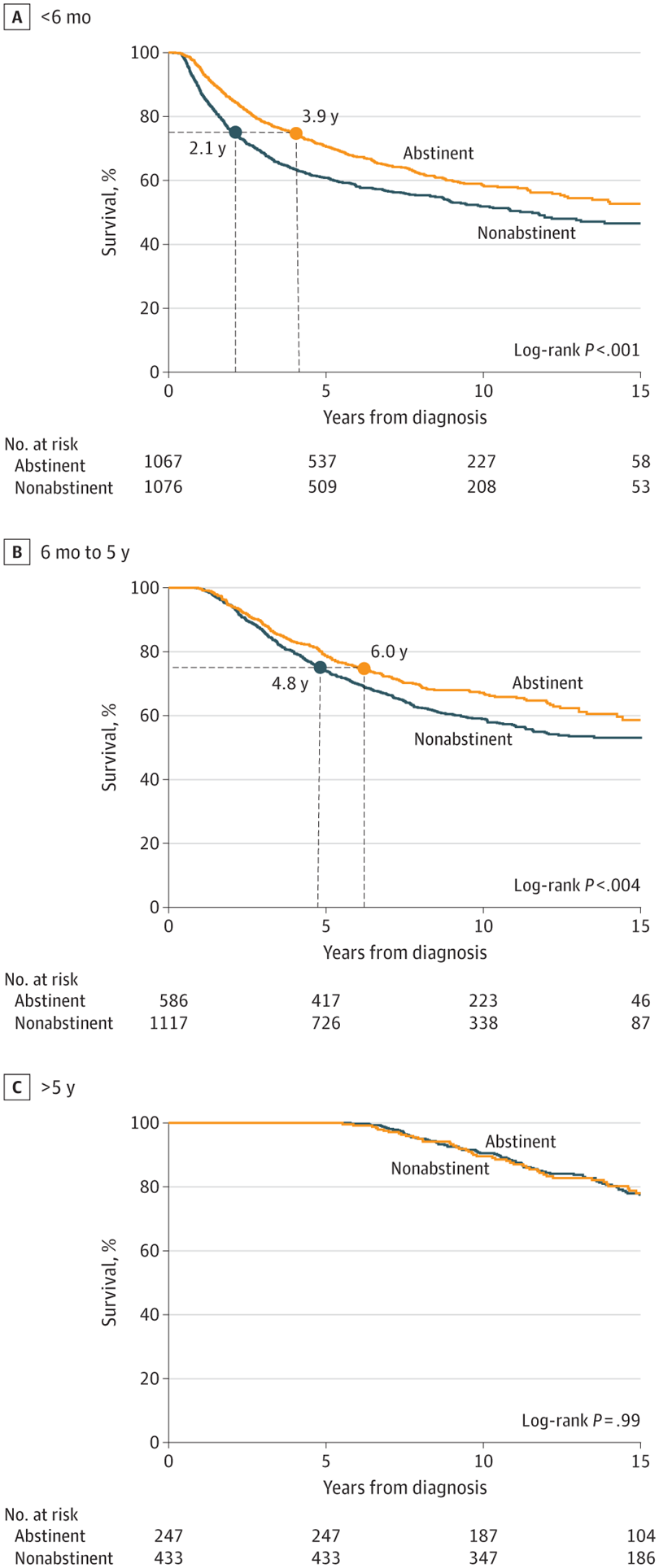 Even After Getting Cancer, Quitting Cigarettes Leads To Greater Longevity
Even After Getting Cancer, Quitting Cigarettes Leads To Greater Longevity