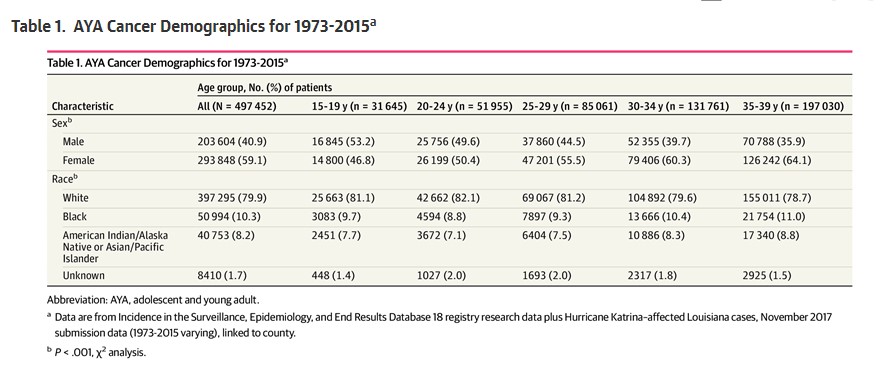
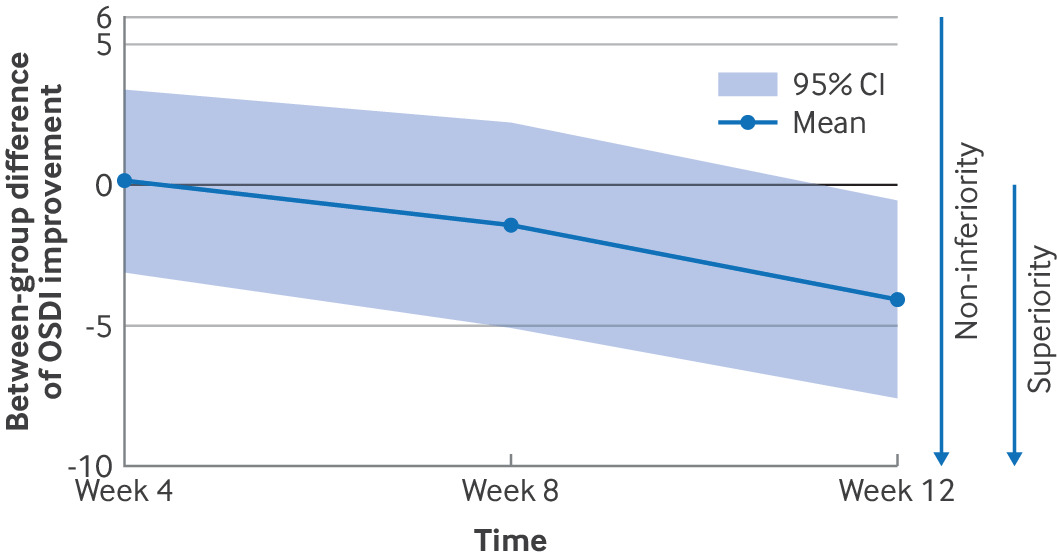
 Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye Disease
Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye DiseaseDry eye disease is a chronic condition estimated to affect around 360 million people. Common symptoms...
 Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A Stroke
Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A StrokeGetting enough sleep is correlated to brain and heart health and after a stroke that is even more...
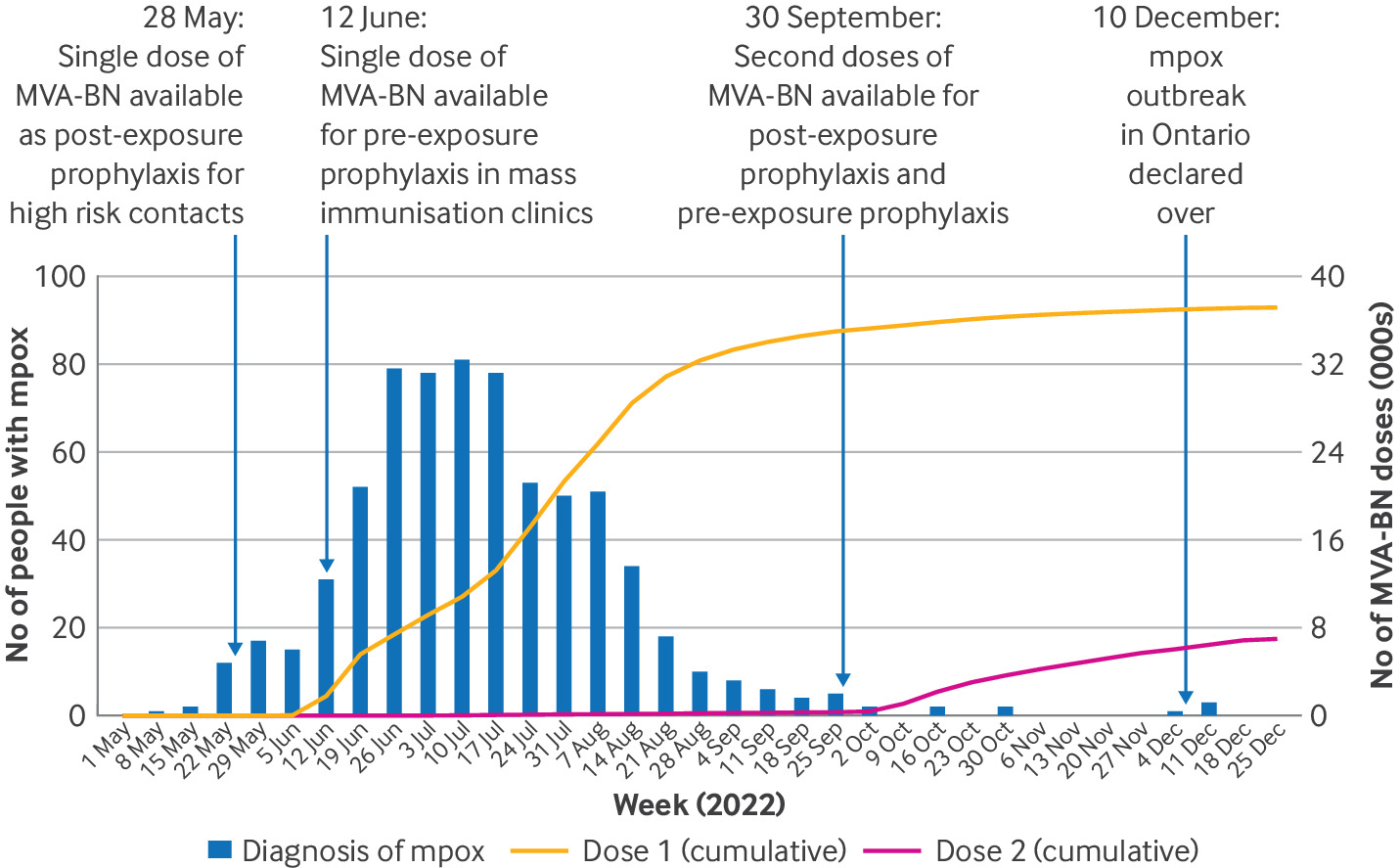 Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing Infection
Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing InfectionA health data simulation has concluded that a single dose of the Modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian...
 C1QL1 - Multiple Sclerosis Research Tackles How The Brain Replaces Lost Myelin
C1QL1 - Multiple Sclerosis Research Tackles How The Brain Replaces Lost MyelinThe neurons in our brains are protected by an insulating layer called myelin. In diseases like...