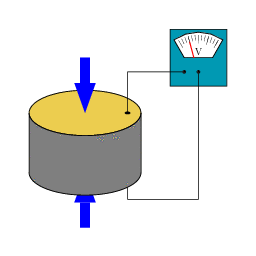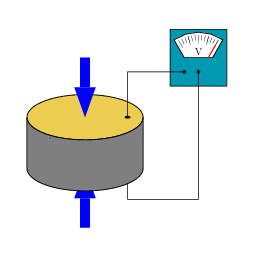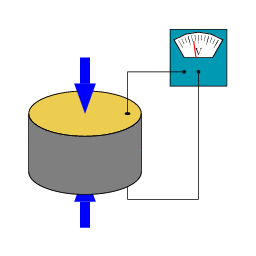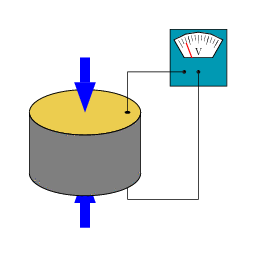
New Magnetocaloric Material Will Allow Magnetic Refrigeration
New Magnetocaloric Material Will Allow Magnetic RefrigerationWhen people think of a refrigerator, magnetism isn't necessarily the first thought that comes to...
 Seeing In The Deep
Seeing In The DeepWith pressures hundreds of times that at sea level and temperatures nearly freezing, it's amazing...
 Ultrafast Laser Inscription Could Enable A 42-Meter Telescope To See The First Galaxies
Ultrafast Laser Inscription Could Enable A 42-Meter Telescope To See The First GalaxiesDemands on telescope technology are rapidly increasing as astronomers look at fainter and fainter...
 What's In The Economic Recovery Bill For Scientists?
What's In The Economic Recovery Bill For Scientists?It's hard to avoid the omnipresent rhetoric being tossed around regarding the economy these days...