Researchers have discovered that the inherent 'handedness' of molecular structures directs the behavior of individual cells and confers them the ability to sense the difference between left and right.
Our bodies are made up of hundreds of different types of cells, each of which performs a unique and highly specialized task. Traditionally, the ability of cells to specialize in a given function was attributed to its genetic code. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that cells do not simply live by a set of inherited or pre-determined instructions. Instead, 'cellular decisions' are made dynamically, much like humans make decisions based on the information provided to us by our senses.
Although cells do not have the ability to see or hear, they do possess sensory structures that allow them to detect and measure various environmental stimuli. The application of mechanical force to the cell, for example, will be felt and the cell will respond accordingly. One of the most prominent cellular responses is to change shape and this property is reflected in the varying shapes of specialized cells.
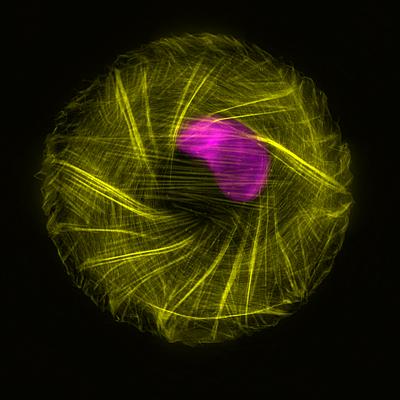
The cytoskeleton (yellow) surrounds the nucleus (purple), displaying L-R asymmetry during cytoskeletal organization. Credit: Mechanobiology Institute, National University of Singapore
Cellular senses have been attributed to various force-sensing cellular structures such as the cytoskeleton. This structure differs significantly from its namesake, the human skeleton, by being highly dynamic and playing roles in addition to the provision of structural support. For example, this network of molecular filaments or cables also generates internal forces that drive shape changes and even motility. As the cytoskeleton develops, individual protein filaments grow and shrink. They bundle together to form thicker fibers, and they move or contract. Each of these processes is collectively known as 'cytoskeleton dynamics'.
The question that has long intrigued scientists is how cytoskeleton dynamics can direct the behavior of different cell types. To investigate this, MBI researchers Professor Alexander Bershadsky and Dr Tee Yee Han, in collaboration with researchers from the USA and Israel, observed the cytoskeleton in cells that were confined to a small circular area, using a technique known as "micro-patterning". This prevented the cells from changing shape and thus provided the researchers an unhindered view of cytoskeleton dynamics.
A surprising find
What was detected came as a surprise to the researchers. A pronounced left-right asymmetry was observed during cytoskeletal organization. This asymmetry, which appeared as a whirlpool, with filaments moving anticlockwise inside the cell, was found to originate from the inherent twist that is present in individual actin filaments. This helical twist occurs naturally as individual actin proteins join together to form the long actin cables that make up overall structure. This seemingly simple property has profound consequences as it suggests that the asymmetry of a single protein is translated to the asymmetric behavior of a whole cell. This is akin to the twist of a screw or bolt directing the function or behavior of the machine in which it is placed.
The ability of cells to distinguish between left and right is a phenomenon that continues to fascinate scientists. It is clear from this study that the asymmetry inherent in molecular structures can define the behavior of whole cells, and this provides new insight into the ability of cells to 'make decisions' based on the mechanical properties of its environment. However, these findings also raise fascinating questions as to whether the same phenomenon can influence the formation and function of our organs, or even affect organism behavior. Indeed relatively simple biological systems, such as cells grown on defined patterns, display a pronounced asymmetry in their movement. At the other extreme, brain function and human cognition is dependent on the asymmetric behavior of nerve cells. The possibility that the inherent asymmetry of molecular structures can define cell, tissue or even organism behavior will undoubtedly drive further studies for years to come.
Published in Cell Biology, http://www.nature.com/ncb/journal/v17/n4/full/ncb3137.html




Comments