Simple models suggested that when high mass stars become hot enough to ionize the gas around them, heating it to thousands of degrees, the gas will quickly expand. But decades ago, astronomers found that regions of ionized gas around young high mass stars remain small (under a third of a light-year) for ten times longer than they should if they were to expand as predicted.
More recent simulations predicted that massive stars continue to collect material via their gravitational attraction, and as a result the regions of ionized gas around a star may not simply grow, but instead interact with the infalling material, causing them to flicker in size and brightness during the main assembly phase of the massive stars, rather than grow continuously.
Observations with the Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) over a 23-year period have confirmed that such flickering actually occurs.
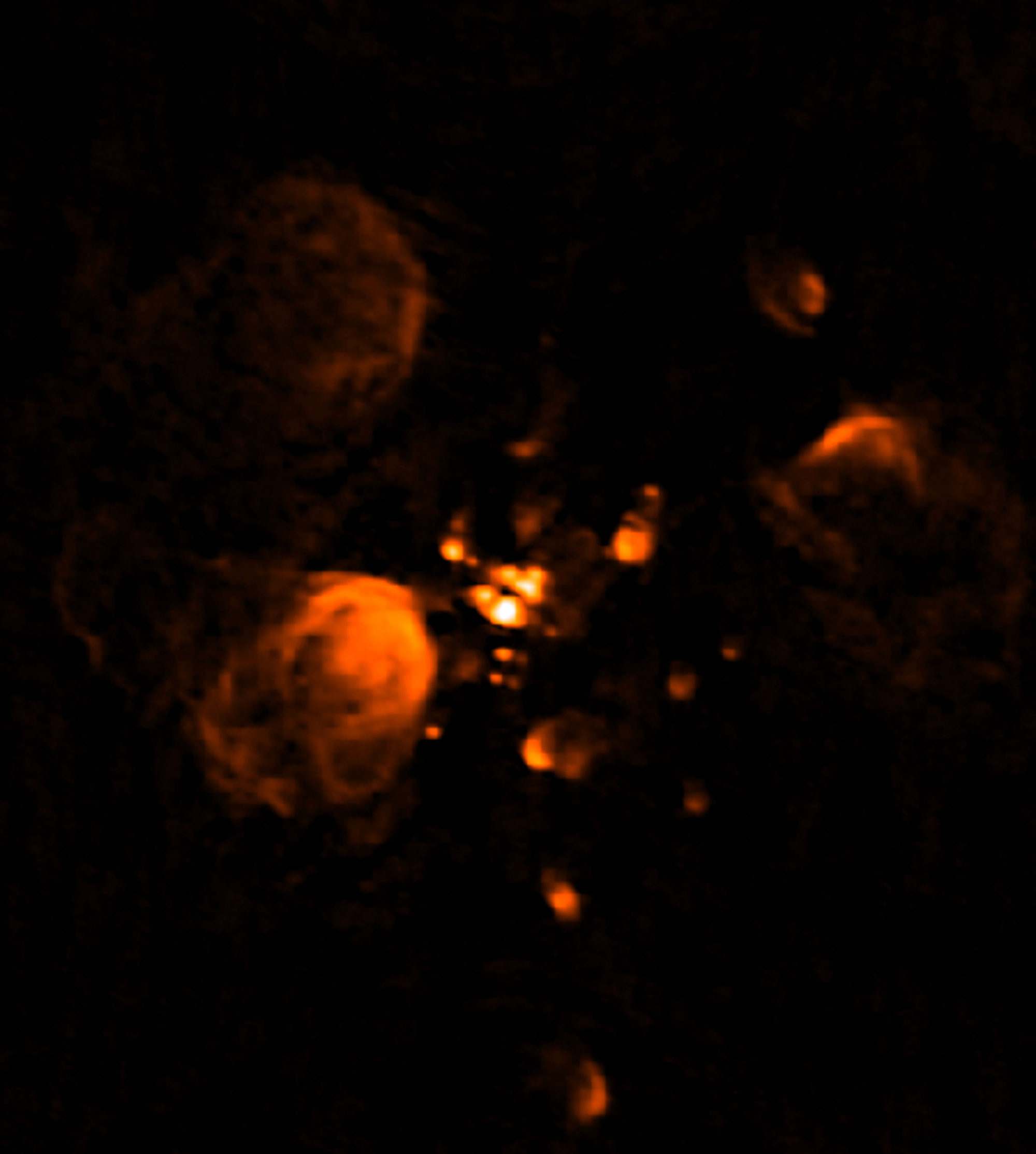
Observations of the massive star forming region Sgr B2 were made with the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) in 1989 and 2012. The VLA has been operational since 1980 and received a major upgrade that was completed in 2011. Credit: NRAO/AUI
Since the VLA was dedicated in 1980, astronomers have observed a large number of regions of ionized hydrogen (so-called H II regions) around high-mass stars that were very small, so small they were termed ultracompact. These early observations conflicted with existing models, which predicted that only the very youngest regions should be so small, and hence, they should be rarely seen. Several models have been proposed to explain this discrepancy, but the recent numerical work made a testable prediction that differed from the other models.
If the cause of the small size was the continued infall of material, these radio sources should flicker and the changes in brightness should be detectable over a 20-year period. “In astronomy it is a rare occurrence to see sources vary on such short timescales, ” said Thomas Peters from Universität Zürich, who led the numerical simulations. “But the regions we predicted to change are huge, almost a thousand times larger than the Solar System!”
The researchers, led by Chris De Pree, professor of astronomy and director of the Bradley Observatory at Agnes Scott College, used VLA observations of the Sagittarius B2 region made in 1989 and again in 2012. This massive star forming region located near the Galactic center contains many small regions of ionized gas around high mass stars, providing a large number of candidates for flickering.
“In the old theoretical model, a high-mass star forms, the HII region lights up and begins to expand, everything was neat and tidy,” De Pree said. “But the group of theorists I am working with were running numerical models that showed accretion was continuing during star formation, and that material was continuing to fall in toward the star after the HII region had formed.”
De Pree’s group chose Sagittarius B2 because the region contains more than 40 ultracompact HII regions. “Since there are so many sources, you can look for changes in relative brightness,” De Pree said. Between 1989 and 2012, four of the HII regions indeed changed in brightness significantly.
“The long term trend is still the same, that HII regions expand with time,” De Pree said. “But in detail, they get brighter or get fainter and then recover. Careful measurements over time can observe this more detailed process.”
Citation: C. G. De Pree, T. Peters, M.-M. Mac Low, D. J. Wilner, W. M. Goss, R. Galván-Madrid, E. R. Keto, R. S. Klessen, and A. Monsrud, Flickering of 1.3 cm Sources in Sgr B2: Toward a Solution to the Ultracompact H II Region Lifetime Problem, The Astrophysical Journal Letters, vol. 781, L36, 2014, doi:10.1088/2041-8205/781/2/L36





Comments