Fibromyalgia is a blanket term for a general painful condition that affects approximately 10 million people in the United States.
Because it lacks consistent symptoms and treatments, some doctors believe an unknown number of instances are psychosomatic but a new paper in PAIN MEDICINE concludes that fibromyalgia may have a rational biological basis, located in the skin.
Fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread deep tissue pain, tenderness in the hands and feet, fatigue, sleep disorders, and cognitive decline. However, routine testing has been largely unable to detect a biological basis for fibromyalgia, so standard diagnosis is instead based upon subjective patient pain ratings, further raising questions about the true nature of the disease.
In many instances, the disorder is considered psychosomatic ("in the head") and even sometimes attributed to patients' imagination or faking illness. Currently approved therapeutics that provide at least partial relief to some fibromyalgia patients act solely within the brain, where imaging techniques have detected hyperactivity of unknown origin referred to as "central sensitization." An underlying cause has not been determined, leaving many physicians still in doubt about the true origins or even the existence of the disorder.
Researchers at Integrated Tissue Dynamics LLC (Intidyn), as part of a fibromyalgia study based at Albany Medical College, say they made have found a biological rationale- a peripheral neurovascular pathology consistently present in the skin of female fibromyalgia patients which may be a driving source of the reported symptoms.
"Instead of being in the brain, the pathology consists of excessive sensory nerve fibers around specialized blood vessel structures located in the palms of the hands," said Dr. Frank L. Rice, President of Intidyn and the senior researcher on the study. "This discovery provides concrete evidence of a fibromyalgia-specific pathology which can now be used for diagnosing the disease, and as a novel starting point for developing more effective therapeutics."
Nerve Endings Come In Many Forms
Three years ago, the scientists wrote in PAIN about an unknown nervous system function among the blood vessels in the skin. As Rice explains, "we analyzed the skin of a particularly interesting patient who lacked all the numerous varieties of sensory nerve endings in the skin that supposedly accounted for our highly sensitive and richly nuanced sense of touch. Interestingly however, this patient had surprisingly normal function in day to day tasks. But, the only sensory endings we detected in his skin were those around the blood vessels.
"We previously thought that these nerve endings were only involved in regulating blood flow at a subconscious level, yet here we had evidence that the blood vessel endings could also contribute to our conscious sense of touch…and also pain."
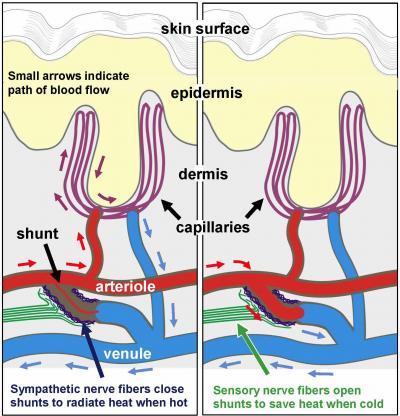
Schematic illustrates the organization of blood vessels and the regulation of blood flow (arrows) in the palm of the hands. Arteriole-venule shunts are small muscular valves that connect directly between an arteriole and a venule to bypass the capillaries. Arrows indicate the direction of blood flow. As shown on the left, in order to radiate heat from our skin when we are hot, activation of the sympathetic nerve fibers close the shunts so that oxygenated blood (red arrows) in the arterioles is forced into the capillaries and deoxygenated (blue arrows) blood returns to the venules. As shown to the right, in order to conserve heat when we are cold, activation of sensory nerve fibers dilate the shunts and the blood bypasses the capillaries. Fibromyalgia patients were found to have an excessive amount of sensory fibers around the shunts. Credit: Frank L. Rice, PhD,Integrated Tissue Dynamics LLC
In collaboration with Albany Medical Center neurologist Dr. Charles E. Argoff, the study primary investigator, and collaborators Dr. James Wyme,r also at Albany Medical College, and Dr. James Storey of Upstate Clinical Research Associates in Albany, NY, the clinical research proposals were funded by Forest Laboratories and Eli Lilly. Both pharmaceutical companies have developed FDA-approved medications with similar functions (Serotonin/Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors, SNRI) that provide at least some degree of relief for many fibromyalgia patients.
"Knowing how these drugs were supposed to work on molecules in the brain," Albrecht added, "we had evidence that similar molecules were involved in the function of nerve endings on the blood vessels. Therefore, we hypothesized that fibromyalgia might involve a pathology in that location". As the results demonstrate, they were correct.
To analyze the nerve endings, they studies small skin biopsies (less than half the size of a pencil eraser) collected from the palms of fibromyalgia patients who were diagnosed and treated by authors of the paper.
The study was limited to women, who have over twice the occurrence of fibromyalgia than men. What the team found was an increase in sensory nerve fibers at specific sites within the blood vessels of the skin. These critical sites are tiny muscular valves, called arteriole-venule (AV) shunts, which form a direct connection between arterioles and venules (see diagram).
As Rice describes their function, "We are all taught that oxygenated blood flows from arterioles to capillaries, which then convey the deoxygenated blood to the venules. The AV shunts in the hand are unique in that they create a bypass of the capillary bed for the major purpose of regulating body temperature."
A Thermostat for the Skin
In humans, these types of shunts are unique to the palms of our hands and soles of our feet which work like the radiator in a car. Under warm conditions, the shunts close down to force blood into the capillaries at the surface of the skin in order to radiate heat from the body, and our hands get sweaty. Under cold conditions, the shunts open wide allowing blood to bypass the capillaries in order to conserve heat, and our hands get cold and put on gloves.
According to co-author Dr. Phillip J. Albrecht, "the excess sensory innervation may itself explain why fibromyalgia patients typically have especially tender and painful hands. But, in addition, since the sensory fibers are responsible for opening the shunts, they would become particularly active under cold conditions, which are generally very bothersome to fibromyalgia patients."
A role in regulating blood flow throughout the body.
Although they are mostly limited to the hands and feet, the shunts likely have another important function which could account for the widespread deep pain, achiness, and fatigue that occurs in fibromyalgia patients.
"In addition to involvement in temperature regulation, an enormous proportion of our blood flow normally goes to our hands and feet. Far more than is needed for their metabolism" noted Dr. Rice. "As such, the hands and the feet act as a reservoir from which blood flow can be diverted to other tissues of the body, such as muscles when we begin to exercise. Therefore, the pathology discovered among these shunts in the hands could be interfering with blood flow to the muscles throughout the body. This mismanaged blood flow could be the source of muscular pain and achiness, and the sense of fatigue which are thought to be due to a build-up of lactic acid and low levels of inflammation fibromyalgia patients. This, in turn, could contribute to the hyperactvity in the brain."
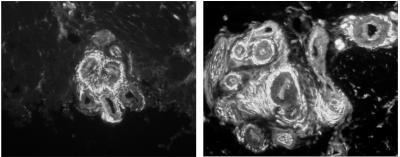
These are digital images of what the arteriole-venule shunts look like in a tiny biopsy of human palmar skin as seen under the microscope. All of the nerve fibers that surround the shunts are white. A shunt in a woman without fibromyalgia is shown to the left and a shunt from a woman with fibromyalgia is shown to the right. The woman with fibromyalgia has an excessive quantity of nerve fibers around her shunt. Credit: Frank L. Rice, PhDIntegrated Tissue Dynamics LLC
Dr. Albrecht also points out that alterations of normal blood flow may underlie other fibromyalgia symptoms, such as non-restful sleep or cognitive dysfunctions. "The data do appear to fit with other published evidence demonstrating blood flow alterations to higher brain centers and the cerebral cortex of fibromyalgia patients" he stated.
Senior Research Chair of the Alan Edwards Center for Pain Research at McGill University, Dr. Gary Bennett, commented after seeing the results that "It is exciting that something has finally been found. We can hope that this new finding will lead to new treatments for fibromyalgia patients who now receive little or no relief from any medicine."
This discovery of a distinct tissue pathology demonstrates that fibromyalgia is not "all in your head", which should provide an enormous relief to fibromyalgia patients, while changing the clinical opinion of the disease and guiding future approaches for successful treatments.
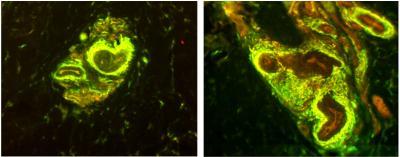
These are digital images showing what the arteriole-venule shunts in a tiny biopsy of human palmar skin look like as seen under the microscope. The processing of the biopsy caused the sensory nerve fibers to appear yellow and the sympathetic nerve fibers to appear green. A shunt in a woman without fibromyalgia is shown to the left and a shunt from a woman with fibromyalgia is shown to the right. The woman with fibromyalgia has an excessive quantity of nerve fibers around her shunt. The increase mostly occurs among the sensory nerve fibers. Credit: Frank L. Rice, PhD, Integrated Tissue Dynamics, LLC




Comments