When you see an article about geckos and their ability to sit upside down, Spider-Man references are sure to follow. And if the topic is that sticky ability in spiders, you will get Spider-Man references and a picture.
Yet even geckos have limits - that's just plain nanophysics.
The fact is, sooner or later the grip is lost, no matter how little force is acting on it. But knowing the limits can have considerable benefits, for instance in the production of graphene - because graphene consists only of one layer of atom, and which must be easily detached from the substrate.

Obligatory Spider-Man reference, by the greatest Spider-Man artist of them all: John Romita. Credit: Marvel Comics Group/Disney
Nils Karlsson of the Division of Mechanics at Linköping University studied both the mechanics of the gecko's leg as well as the adhesion of its foot to the substrate. The gecko's foot has five toes, all with transverse lamellae. A scanning electron microscope shows that these lamellae consist of a number of small hair-like setae, each with a little film at the end, which resembles a small spatula. These spatulae, roughly 10 nm thick, are what adheres to the substrate.
"At the nano level, conditions are a bit different. The movement of the molecules is negligible in our macroscopic world, but it's not in the nano world. Nils Karlsson's graduation project suggested that heat, and consequently the movement of the molecules, has an effect on the adhesion of these spatulae. We wanted to do further analyses, and calculate what actually happens," explains co-author Stefan Lindström.
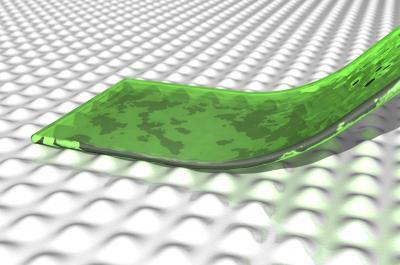
A thin film is in contact with an uneven surface. Credit: Stefan Lindström and others
They refined the calculations, so they applied to a thin film in contact with an uneven surface. So, the film only contacts the uppermost parts of the uneven surface. The researchers also chose to limit the calculations to the type of weak forces that exist between all atoms and molecules – van der Waals forces.
"It's true, they are small, but they are always there and we know that they are extremely reliant on distance," says co-author Lars Johansson.
This means that the force is much stronger where the film is very close to a single high point, than when it is quite close to a number of high points. Then, when the film detaches, it does this point by point. This is because both contact surfaces are moving – vibrating. These are tiny movements, but at some stage the movements are in sync, so the surfaces actually lose contact. Then the van der Waals force is so small that the film releases.
"So in reality, we can detach a thin film from the substrate simply by waiting for the right moment. This doesn't require a great deal of force. The part of the film that remains on the substrate vibrates constantly, and the harder I pull on this part, the faster the film will detach. But how long it takes for the film to detach also depends on the structure of the substrate and the film's stiffness," says Lindström.
In practice this means that even a small force over a long period will cause the film, or for that matter Spider-Man's foot, to lose its grip. Which is fine for a superhero, who can scoot off, but maybe not so good for a fastening system. Still, in the right application, this knowledge can be of great industrial benefit.




Comments