Historical acid deposits have greatly reduced calcium levels in Canadian lakes and that is dramatically impacting populations of calcium-rich plankton such as Daphnia - water fleas that dominate these ecosystems.
Falling calcium levels mean fewer Daphnia get the nutrients they need to survive and reproduce. Because they then consume less food and are more susceptible to predators, they leave more algae for other organisms to feed on and a small jelly-clad organism called Holopedium is taking advantage of it.
Holopedium are plankton competitors of the Daphnia that use less calcium - they also have a jelly coat that affords them greater protection from predators. Due to this, lakes across eastern Canada have seen Holopedium populations explode in the last thirty years; particularly in lakes in the province of Ontario that have seen a recent Eurasian invasion of the spiny water flea - which also favors hunting Daphnia, affording Holopedium even more room in these ecosystems to expand.
Researchers say the average population of these small invertebrate jellies in many Ontario lakes doubled between the mid-1980s and the mid-2000s. They warn that the increasing 'jellification' of Canada's lakes will prevent vital nutrients being passed up the food chain to fish stocks, as well as clogging filtration systems that help the lakes contribute drinking water to many residents in these areas.

Holopedium from a lake in the Muskoka-Haliburton region of Ontario. Credit: Ron Ingram, Ontario Ministry of the Environment
The team used data from monthly surveys of lakes that recorded water chemistry and plankton populations for over 30 years, and used the latest statistical techniques to map all the cause-and-effect relationships in these ecosystems to determine that falling water calcium was causing the jelly boom. The results are published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
"As calcium declines, the increasing concentrations of jelly in the middle of these lakes will reduce energy and nutrient transport right across the food chain, and will likely impede the withdrawal of lake water for residential, municipal and industrial uses," said study co-author Dr Andrew Tanentzap, from the University of Cambridge's Department of Plant Sciences.
"In Ontario, 20% of government-monitored drinking water systems now come from landscapes containing lakes with depleted calcium concentrations that favour Holopedium, and this is only set to increase."
Historically, a lot of acid was deposited throughout the northern hemisphere due to industrialisation. The acid displaced calcium from soil, says Tanentzap. Over a long period, this process pushed all the calcium out of drainage areas that feed these lakes, causing dramatic declines in the water calcium levels.
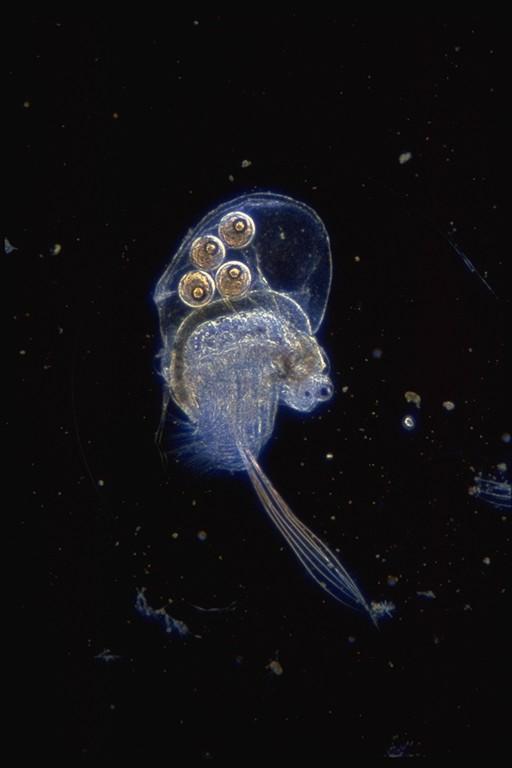
Holopedium. Credit: Michael Arts, Canada Centre for Inland Waters
"Pollution control may have stopped acid deposits in the landscape, but it's only now that we are discovering the damage wasn't entirely reversed," he said.
Daphniids have a heavily calcified exoskeleton, so need much higher levels of calcium and phosphorous. In low calcium water, Daphnia are much more vulnerable to at least one key predator - the larval phantom midge, or Chaoborus - as their ability to produce defences such as larger bodies, stronger exoskeletons and projecting neck teeth is compromised. Additionally, the Daphniids phosphorous requirements mean they need to eat a lot more.
Holopedium, however, have no exoskeleton, and require only half the phosphorous of Daphnia and just one-tenth the amount of calcium, and the jelly capsule in which Holopedium are contained largely protects them from the predators that live on plankton of this size.
Calcium loss isn't the only bad news for Daphniids. The team suggest that climate change is causing oxygen decline deep in the lakes, creating better conditions and increasing populations of larval midges - the main predator of Daphnia.
The team also investigated how far back the jellification of these lakes began. By analysing sediment cores and fossil records, they show that Holopedium have been steadily increasing ever since around 1850 - a time of early industrialisation and consequent acid deposit increases. But the process really gathered pace from the 1980s onwards.
"It may take thousands of years to return to historic lake water calcium concentrations solely from natural weathering of surrounding watersheds," said Tanentzap.
"In the meanwhile, while we've stopped acid rain and improved the pH of many of these lakes, we cannot claim complete recovery from acidification. Instead, we many have pushed these lakes into an entirely new ecological state."




Comments