If we could start 2020 all over again, the world would be satisfied if the big worry was wildfires and whether or not cat litter had a Non-GMO Project label.
Instead, we got a coronavirus from Wuhan, China, and a COVID-19 disease that isn't stopping any time soon. But science marches on, and we also have machine learning helping to grow artificial organs.
One of the glaring errors in the controversial United Nations IPCC report critical of agriculture was that it used the Greenhouse Gas Protocol yet ignored the carbon sequestration of crops. A politically neutral examination of the science shows that
agriculture is nowhere near as big a problem in emissions as activists have claimed.
The origin of carbon in the Milky Way is a mystery but one source of many elements is not: Dying white dwarfs. As those dying stars pass into oblivion, they sprinkle their ashes into the cosmos. These ashes, spread via stellar winds, are enriched with many different chemical elements, including carbon.
The origin of carbon, an element essential to life on Earth, in the Milky Way galaxy is primarily speculation: some are in favor of the idea that low-mass stars blew off their carbon-rich envelopes by stellar winds became white dwarfs, while others place the major site of carbon's synthesis in the winds of massive stars that eventually exploded as supernovae.
Is citizen science a luxury for wealthy countries? Pastimes like bird watching, which require very little wealth to start, are more common in developed lands, but it would help fill the gaps in science elsewhere.
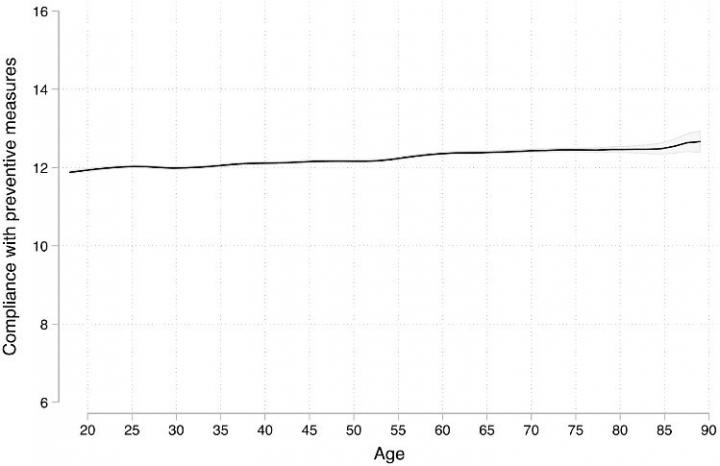
Surveys are not behavior but if surveys are any indication, elderly people are not willing to self-isolate, even knowing they are at greatest risk of getting COVID-19, the newest mutation of the coronavirus that originated in Wuhan, China, and and spread worldwide.
Survey results from 27 countries find that elderly people are not more compliant with COVID-19 preventive measures and not more willing to isolate when asked, even though it is established that older adults appear are far more likely to be hospitalized or die from the disease.
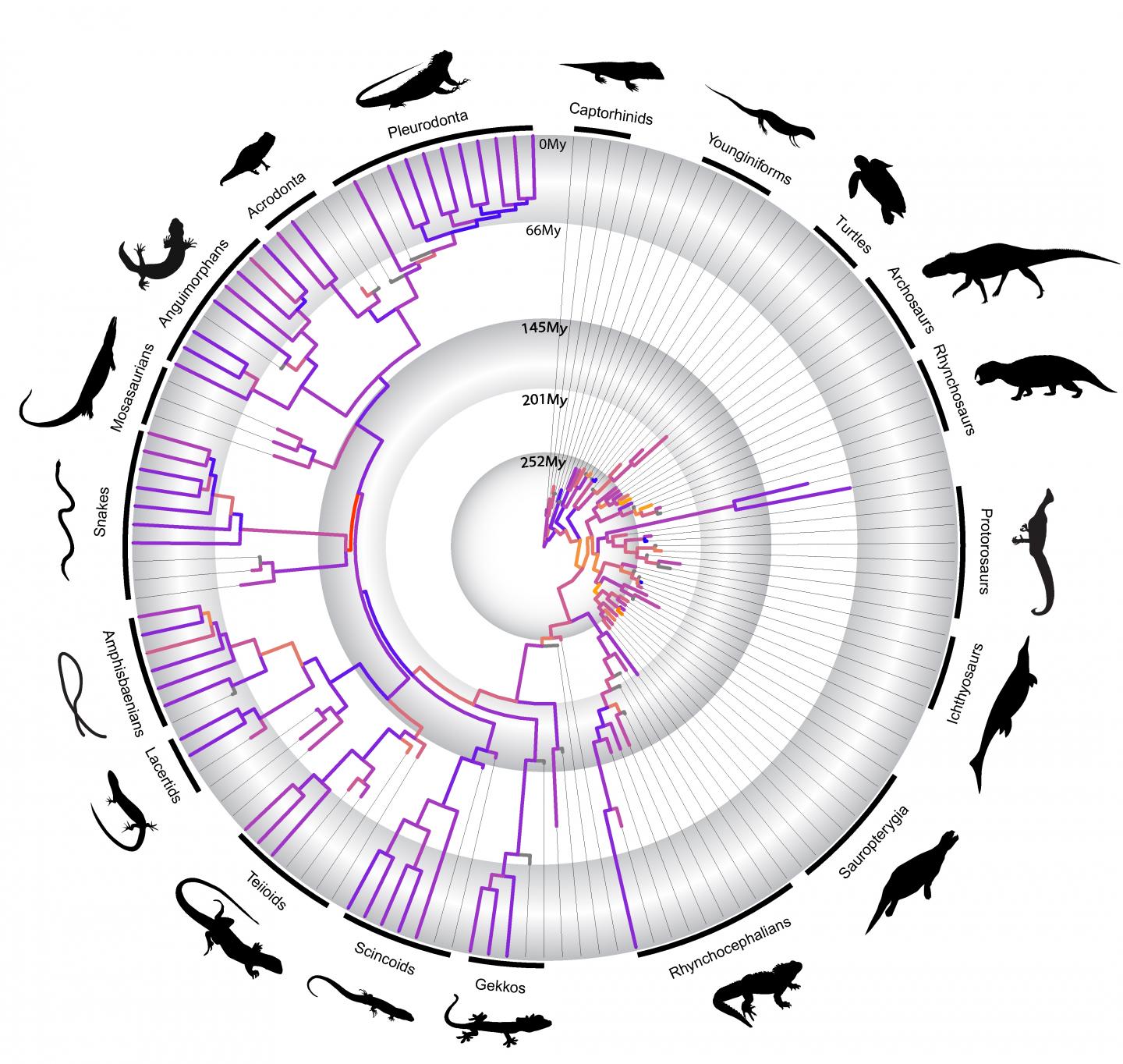
Though we've learned a lot about evolution in the last 150 years, when it comes to the details, some fundamental questions remain unanswered. Such as when and how extremely diverse groups of animals such as reptiles first evolved. For seventy-five years, adaptive radiation, the relatively fast evolution of many species from a single common ancestor, has been considered a major cause of biological diversity.
This has even been for the origins of major body plans (structural and developmental characteristics that identify a group of animals) and new lineages. Yet examining these rapid rates of evolution has been constrained by the methods used and the amount of data available.
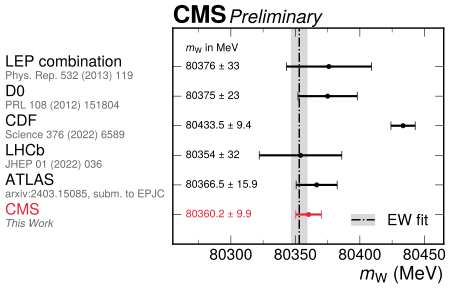 Standard Model Stands? New Measurement Of The W Mass At The LHC
Standard Model Stands? New Measurement Of The W Mass At The LHC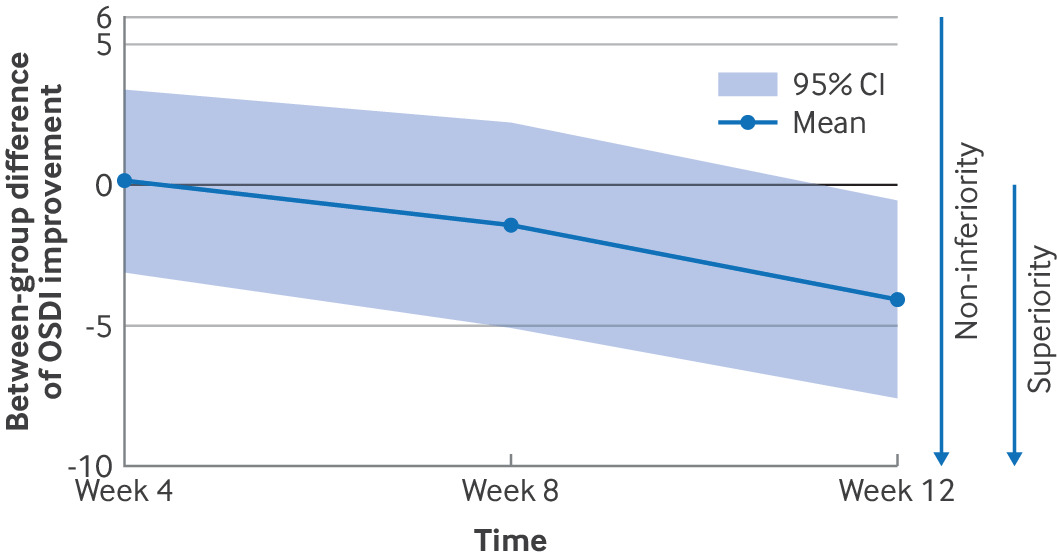 Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye Disease
Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye Disease Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A Stroke
Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A Stroke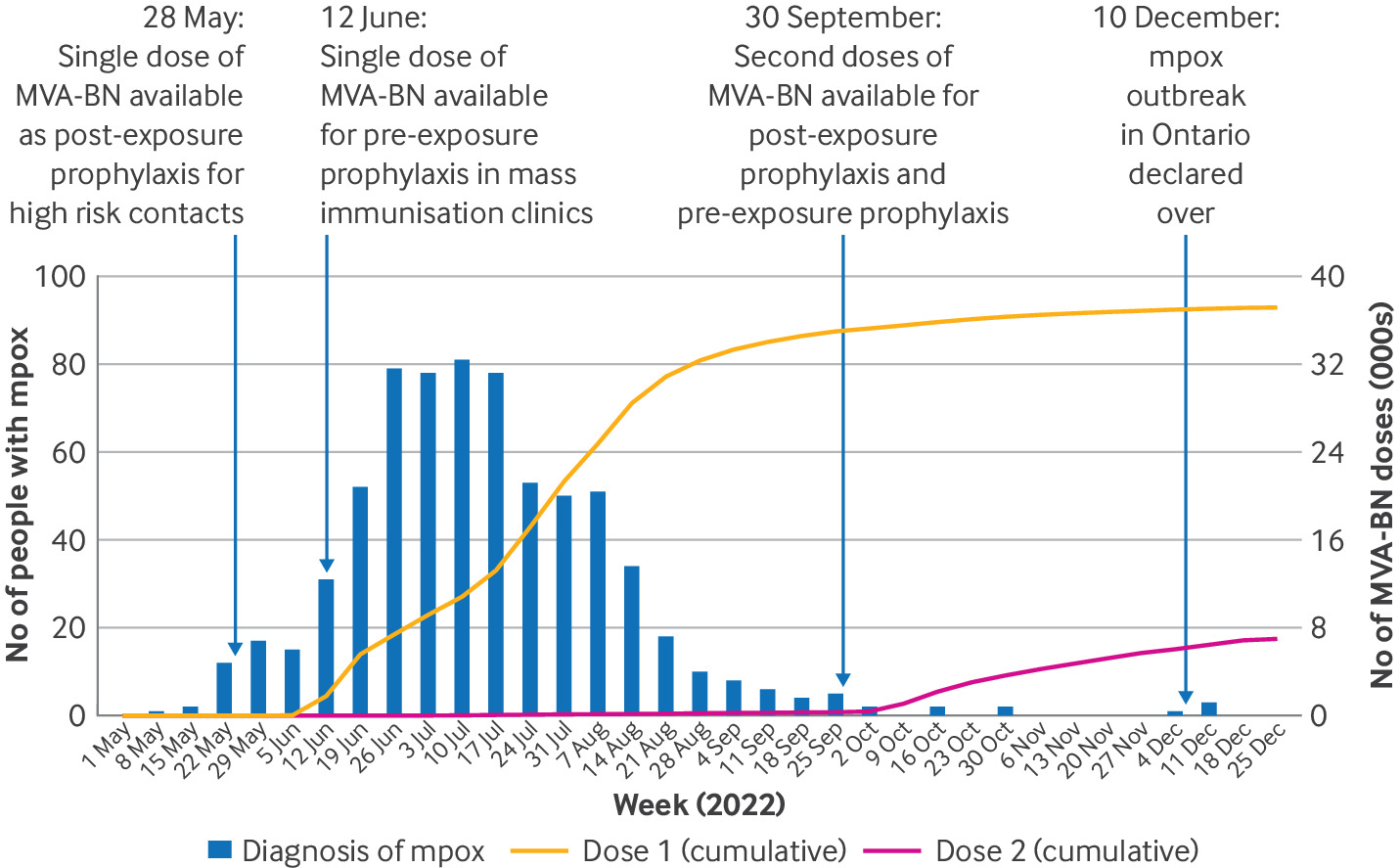 Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing Infection
Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing Infection