 Standard Model Stands? New Measurement Of The W Mass At The LHC
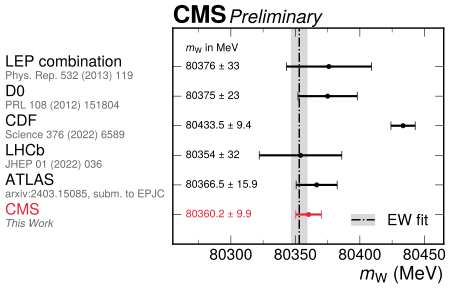
Standard Model Stands? New Measurement Of The W Mass At The LHCTheories in physics come and go, some are popular yet entirely speculative and fade away quickly...
 Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye Disease
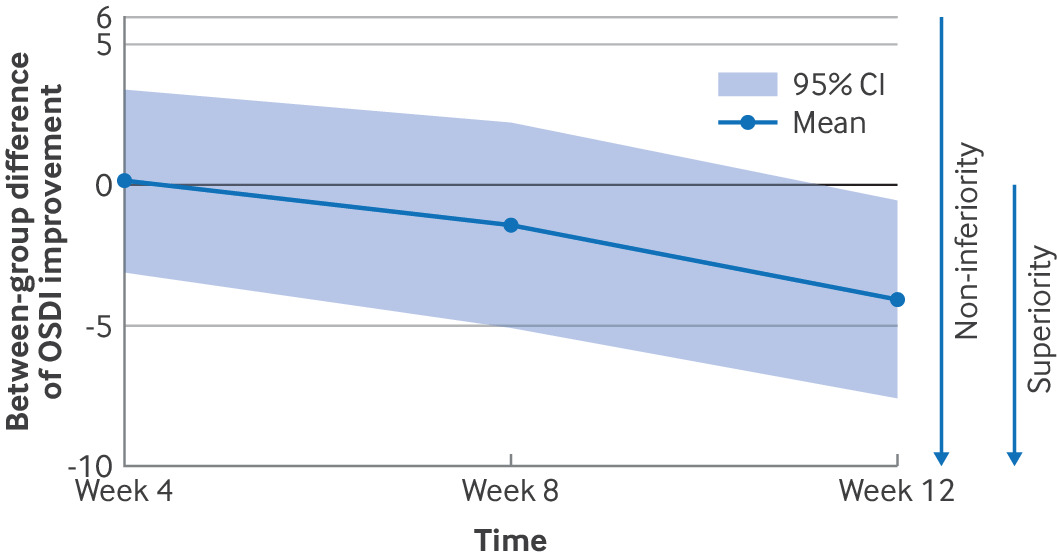
Laughter Exercise Could Be Treatment For Dry Eye DiseaseDry eye disease is a chronic condition estimated to affect around 360 million people. Common symptoms...
 Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A Stroke
Normal Sleep Duration 50% Less Common After A StrokeGetting enough sleep is correlated to brain and heart health and after a stroke that is even more...
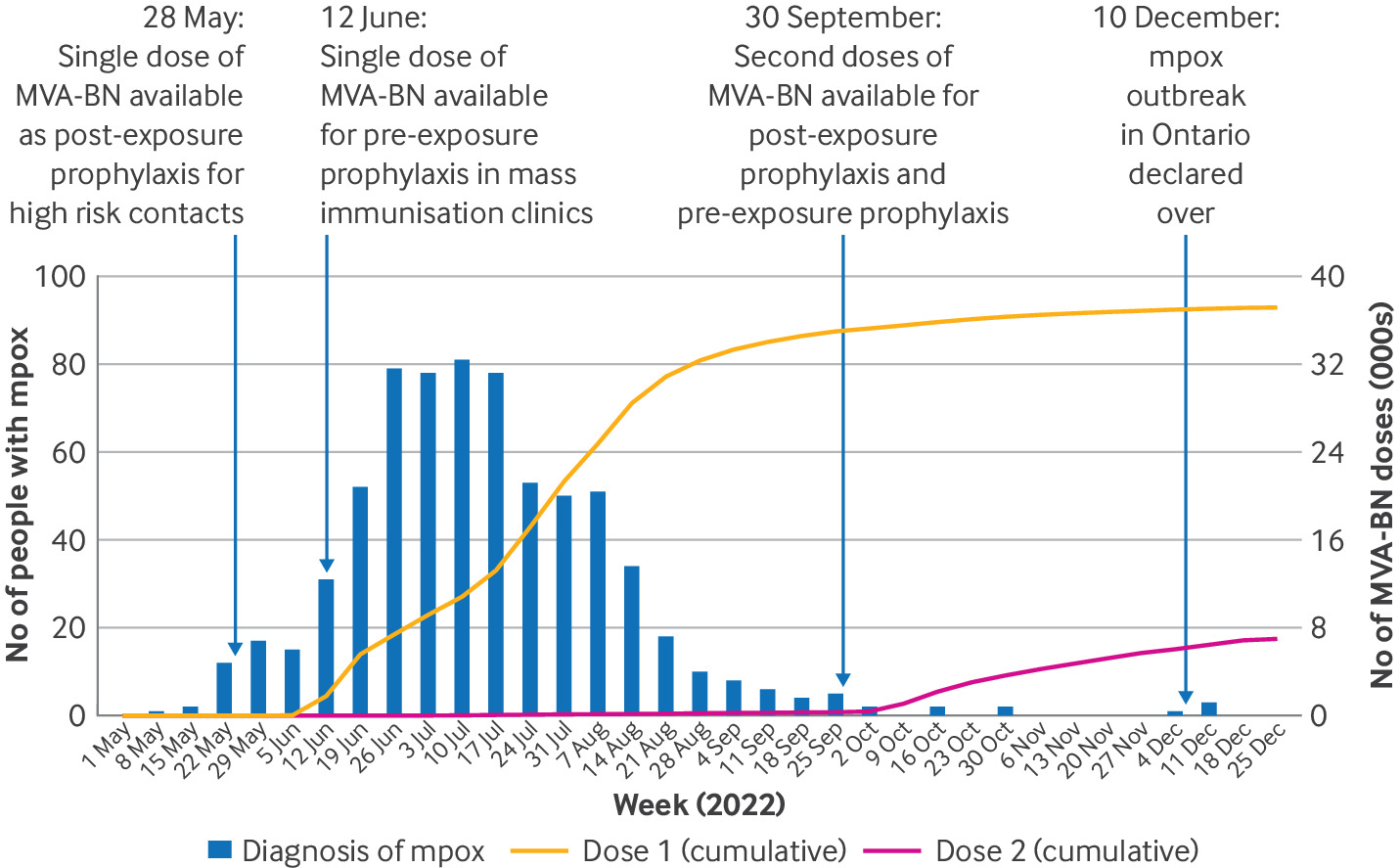 Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing Infection
Mpox Vaccine Effective In Preventing InfectionA health data simulation has concluded that a single dose of the Modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian...