Mind readers have long been the domain of folklore and science fiction. But some new findings demonstrate the power of computational modeling to improve our understanding of how the brain processes information and thoughts and it brings scientists closer to knowing how specific thoughts activate our brains.
In their most recent work a computer scientist, Tom Mitchell, and a cognitive neuroscientist, Marcel Just, both of Carnegie Mellon University, used fMRI data to develop a sophisticated computational model that can predict the brain activation patterns associated with concrete nouns, or things that we experience through our senses, even if the computer did not already have the fMRI data for that specific noun.
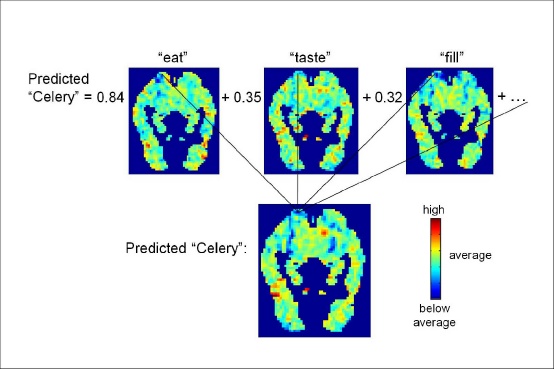
The researchers first built a model that took the fMRI activation patterns for 60 concrete nouns broken down into 12 categories including animals, body parts, buildings, clothing, insects, vehicles and vegetables. The model also analyzed a text corpus, or a set of texts that contained more than a trillion words, noting how each noun was used in relation to a set of 25 verbs associated with sensory or motor functions. Combining the brain scan information with the analysis of the text corpus, the computer then predicted the brain activity pattern of thousands of other concrete nouns.
In cases where the actual activation patterns were known, the researchers found that the accuracy of the computer model's predictions was significantly better than chance. The computer can effectively predict what each participant's brain activation patterns would look like when each thought about these words, even without having seen the patterns associated with those words in advance.
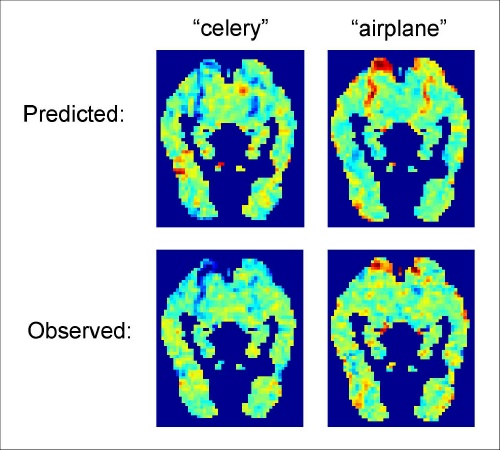
"We believe we have identified a number of the basic building blocks that the brain uses to represent meaning," said Mitchell. "Coupled with computational methods that capture the meaning of a word by how it is used in text files, these building blocks can be assembled to predict neural activation patterns for any concrete noun. And we have found that these predictions are quite accurate for words where fMRI data is available to test them."
Just said the computational model provides insight into the nature of human thought. "We are fundamentally perceivers and actors," he said. "So the brain represents the meaning of a concrete noun in areas of the brain associated with how people sense it or manipulate it. The meaning of an apple, for instance, is represented in brain areas responsible for tasting, for smelling, for chewing. An apple is what you do with it. Our work is a small but important step in breaking the brain's code."
In addition to representations in these sensory-motor areas of the brain, the Carnegie Mellon researchers found significant activation in other areas, including frontal areas associated with planning functions and long-term memory. When someone thinks of an apple, for instance, this might trigger memories of the last time the person ate an apple, or initiate thoughts about how to obtain an apple.
"This suggests a theory of meaning based on brain function," Just added.
The work could eventually lead to the use of brain scans to identify thoughts and could have applications in the study of autism, disorders of thought such as paranoid schizophrenia, and semantic dementias such as Pick's disease.
Officials at NSF say they are excited and intrigued by these findings. "This has been an interesting project to watch," said Kenneth Whang, a program officer at NSF who is responsible for the grant to Mitchell and Just. "They started with some fundamental ideas from machine learning about how to get the most out of fMRI data, and now they've not only shown the power of their computational approach, but also made headway on one of the most important problems in the understanding of language in the brain."
Whang believes that Mitchell and Just's research will stimulate further research in the field of computational neuroscience. "This opens up all sorts of new possibilities for looking into the fine structure of how patterns of brain activity relate to human thought processes."
-NSF-




Comments