You're probably not racist. As the world has gotten smaller, race as a bias has become less of a thing. Yet there is a test - the Implicit Association Test - that is guaranteed to show you are racist and weak observational studies that use it end up in a lot of mainstream media stories.
Now there may be a way to cure it.
The rubber hand illusion is designed to allow people to experience being different virtually. Now it can make you feel like you have the body of someone of a different race, age, or sex. So whatever stereotypes you have - and you have them - may at least be changed due to this kind of virtual body swapping. Would that change the way you feel about yourself or the way that you stereotype different social groups? A new paper tricks white brains into thinking they are inhabiting black bodies and makes adults feel like they had children's bodies. The authors believe this has important implications for approaching phenomena such as race and gender discrimination.

(A) The Rubber Hand Illusion: Light-skinned Caucasian participants observe a dark-skinned rubber hand being stimulated in synchrony with their own unseen hand. This elicits a shift of body ownership to incorporate the other-race limb. Adapted and reproduced, with permission, from reference [9].
(B) The Enfacement Illusion: Participants viewed the face of a racial outgroup member being stimulated in synchrony with their own to induce a sense of ownership over the observed face (see reference [14]).
(C) Immersive Virtual Reality: (i) A participant wears a wide field-of-view stereo head-tracked head-mounted display and a motion capture suit for real-time body tracking. (ii) This is the participant's view of the situation, whereby she can see her virtual body both directly and reflected in the mirror, in stereo as shown. The body she sees could be dark-skinned, light-skinned, or purple; in this case, the virtual body is dark skinned whereas she is light skinned. Credit: Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Maister et al.
Negative attitudes about others are often formed at a young age, and they're thought to remain relatively stable throughout adulthood. However, few studies have examined whether implicit social biases can change. In recent years, however, Professor Manos Tsakiris of the Royal Holloway University of London and Professor Mel Slater of University College London and the University of Barcelona have developed ways to expose participants to bodily illusions that induce ownership over a body different from their own with respect to race, age, or gender.
For white people who were made to feel that they had black bodies, their unconscious biases against black people diminished. And adults who felt as if they had children's bodies processed perceptual information and aspects of themselves as being more childlike.
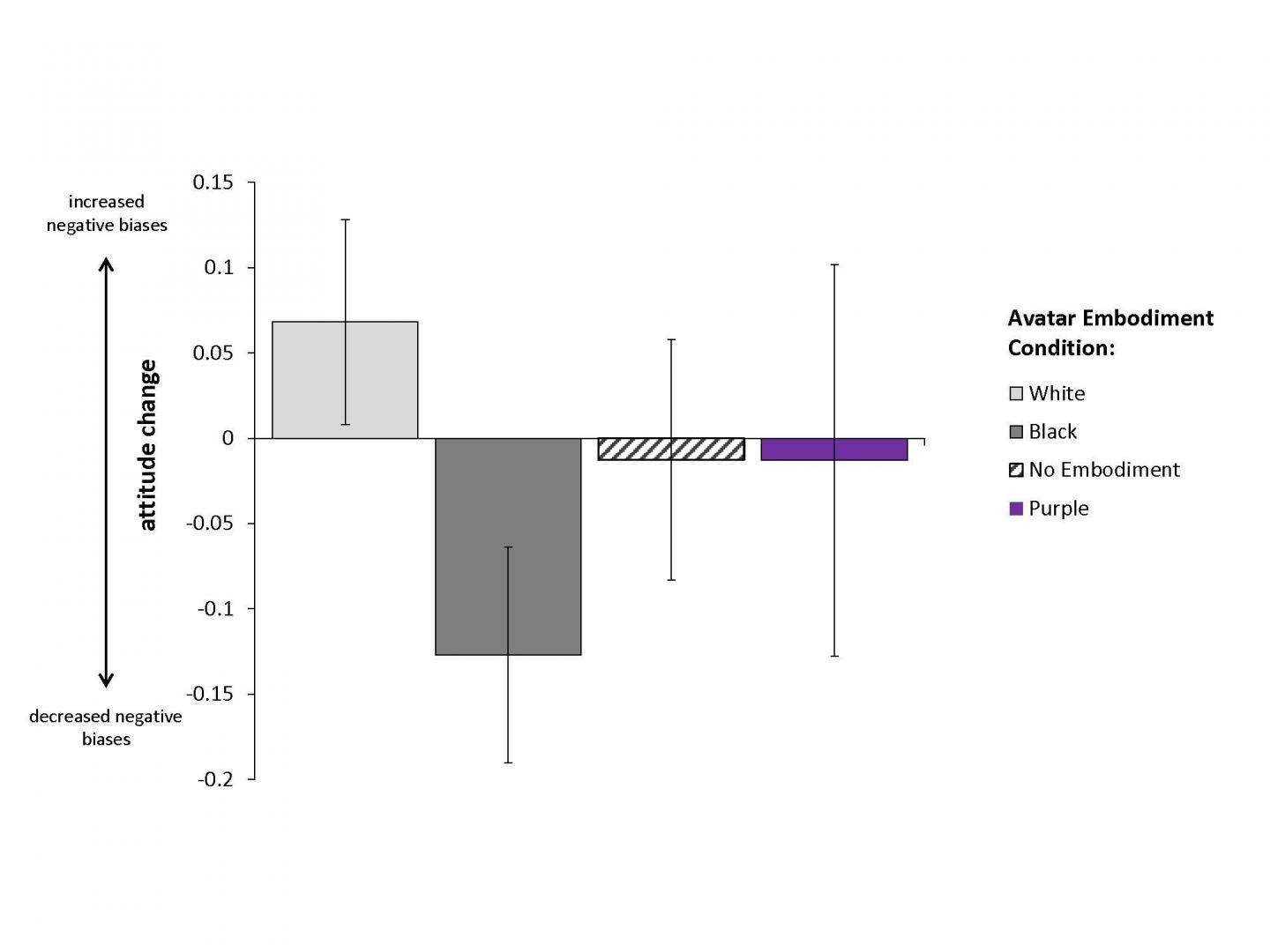
Light-skinned Caucasian participants took part in a between-groups experiment where they occupied a white (A) or black (B) body in a virtual environment. They could see their body from a first-person perspective when they looked down, as well as in a virtual mirror (see Figure 1C, ii). Two control groups were also included -- in these conditions, participants either had no virtual body (C), or the body was of an unnatural purple color (D) to control for general dissimilarity to their own skin. Participants' implicit racial biases were measured before and after embodiment. Participants who embodied a black avatar showed a decrease in their implicit biases against black individuals, which was significantly greater than for those who embodied a white avatar. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Credit: Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Maister et al.
"Our findings are important as they motivate a new research area into how self-identity is constructed and how the boundaries between 'ingroups' and 'outgroups' might be altered," says Tsakiris. "More importantly though, from a societal point of view, our methods and findings might help us understand how to approach phenomena such as racism, religious hatred, and gender inequality discrimination, since the methods offer the opportunity for people to experience the world from the perspective of someone different from themselves."
While there is no simple "cure" for racism or other biases, "the research shows that integration of different sensory signals can allow the brain to update its model of the body and cause people to change their attitudes about others," says Slater.





Comments