First principles are calculations that rely on established mathematical laws of nature without additional assumptions or special models.
But when it comes to the early universe, what are those first principles? We're talking really ab initio - "from the beginning" - as in from the beginning of time onward.
In the beginning, the cosmos experienced rapid inflation, electrons and protons floated free from each other, the universe transitioned from complete darkness to light, and enormous stars formed and exploded to start a cascade of events leading to our present-day universe.
Milos Milosavljevic, Chalence Safranek-Shrader and Volker Bromm at The University of Texas at Austin, reported the results of numerical simulations which seek to chart the forces of the universe in its first hundreds of millions of years.
They say their results refine how the first galaxies formed, and in particular, how metals in the stellar nurseries influenced the characteristics of the stars in the first galaxies.

This simulation shows hydrodynamic instability triggered by rapid cooling in a heavy-element-enriched cosmic dark matter halo when the universe was only 300 million years old. The instability drives turbulence which breaks the flow into fragments. Some fragments undergo gravitational collapse and set to fragment into progressively smaller units. From left to right and top to bottom, the six panels show projections of gas density, and the horizontal bar has length 1 pc = 3.26 light years. Credit: Chalence Safranek-Shrader, Milos Milosavljevic, and Volker Bromm, The University of Texas at Austin
"The universe formed at first with just hydrogen and helium," Milosavljevic said. "But then the very first stars cooked metals and after those stars exploded, the metals were dispersed into ambient space."
Eventually the ejected metals fell back into the gravitational fields of the dark matter haloes, where they formed the second generation of stars. However, the first generation of metals ejected from supernovae did not mix in space uniformly.
"It's as if you have coffee and cream but you don't stir it, and you don't wait for a long enough time," he explained. "You would drink some cream and coffee but not coffee with cream. There will be thin sheets of coffee and cream."
According to Milosavljevic, subtle effects like these governed the evolution of early galaxies. Some stars formed that were rich in metals, while others were metal-poor. Generally there was a spread in stellar chemical abundances because of the incomplete mixing.
Another factor that influenced the evolution of galaxies was how the heavier elements emerged from the originating blast. Instead of the neat spherical blast wave that researchers presumed before, the ejection of metals from a supernova was most likely a messy process with blobs of shrapnel shooting in every direction.
"Modeling these blobs properly is very important for understanding where metals ultimately go," Milosavljevic said.
In astronomical terms, early in the universe translates to very far away. Those fugitive first galaxies are unbelievably distant from us now, if they haven't been incorporated into more recently-formed galaxies already. But many believe the early galaxies lie at a distance that we will be able to observe with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), set to launch in 2018. This makes Milosavljevic and his team's cosmological simulations timely.
"Should the James Webb Space Telescope integrate the image in one spot for a long time or should it mosaic its survey to look at a larger area?" Milosavljevic asked. "We want to recommend strategies for the JWST."
Telescopes on the ground will perform follow-up studies of the phenomena that JWST detects. But to do so, scientists need to know how to interpret JWST's observations and develop a protocol for following up with ground-based telescopes.
Milosavljevic and others' cosmological simulations will help determine where the Space Telescope will look, what it will look for, and what to do once a given signal is observed.
Distant objects, born at a given moment in cosmic history, have a tell-tale signature — spectra or light curves. Like isotopes in carbon dating, these signatures help astronomers recognize and date phenomenon in deep space. In the absence of any observations, simulations are the best way of predicting these light signatures.
"We are anticipating observations until they become available in the future," Milosavljevic said.
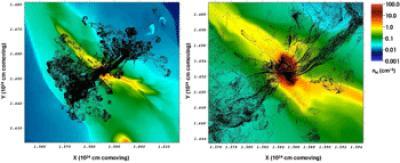
This simulation shows heavy-element-bearing sheets of an exploding star's debris streaming into the center of a cosmic dark matter halo. Upon arriving in the center, the streams will enable the formation of the first low-mass stars, when the universe was still only about 200 million years old. Credit: Jeremy Ritter, Milos Milosavljevic, and Volker Bromm, The University of Texas at Austin
If done correctly, such simulations can mimic the dynamics of the universe over billions of years, and emerge with results that look something like what we see — or hope to see with new farther-reaching telescopes.
"This is a really exciting time for the field of cosmology," astronomer and Nobel Laureate Saul Perlmutter said in his keynote address at the Supercomputing '13 conference in November. "We are now ready to collect, simulate and analyze the next level of precision data... there's more to high performance computing science than we have yet accomplished."
In addition to the practical goals of guiding the James Webb Space Telescope, the effort to understand these very early stars in the first galaxies has another function: to help tell the story of how our solar system came to be.
The current state of the universe is determined by the violent evolutions of the generations of stars that came before. Each generation of stars (or "population," in astronomy terms) has its own characteristics, based on the environment it was created in.
The Population III stars, the earliest that formed, are thought to have been massive and gaseous, consisting initially of hydrogen and helium. These stars ultimately collapsed and seeded new, smaller, stars that clustered into the first galaxies. These in turn exploded again, creating the conditions of Population I stars like our own, chock full of materials that enable life. How stars and galaxies evolved from one stage to another is still a much-debated question.
"All of this was happening when the universe was very young, only a few hundred million years old," Milosavljevic said. "And to make things more difficult, stars — like people — change. Every hundred million years, every 10 million years — it's like a kid growing up, all the time something new is happening."
Simulating the universe from birth to its current age, Milosavljevic and his team's investigations help disentangle how galaxies changed over time, and provide a better sense of what came before us and how we came to be.
Said Nigel Sharp, program director in the Division of Astronomical Sciences at the National Science Foundation: "These are novel studies using methods often ignored by other efforts, but of great importance as they impact so much of what happens in later cosmology and galaxy studies."
Source: University of Texas at Austin, Texas Advanced Computing Center





Comments