By the time they turn two, most children have had respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and suffered symptoms no worse than a bad cold.
Yet for some children, especially premature babies and those with underlying health conditions, RSV can lead to pneumonia and bronchitis, hospitalization and have long-term consequences.
RSV can be difficult to study. For one thing, the infectious particle can take different forms, ranging from 10-micron filaments to ordinary spheres. The virus can insert more than one genome into the host cells and the RNA orientation and structure are disordered, which makes it difficult to characterize.
A new technique for studying the structure of the RSV virion - direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) imaging - and the activity of RSV in living cells could help researchers unlock the secrets of the virus, including how it enters cells, how it replicates, how many genomes it inserts into its hosts – and perhaps why certain lung cells escape the infection relatively unscathed. That could provide scientists information they need to develop new antiviral drugs and perhaps even a vaccine to prevent severe RSV infections.
"We want to develop tools that would allow us to get at how the virus really works," said Philip Santangelo, an associate professor in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University. "We really need to be able to follow the infection in a single living cell without affecting how the virus infects its hosts, and this technology should allow us to do that.
"We've shown that we can tag the genome using our probes. What we've learned from this is that the genome does get incorporated into the virion, and that the virus particles created are infectious. We were able to characterize some aspects of the virus particle itself at super-resolution, down to 20 nanometers, using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) imaging."
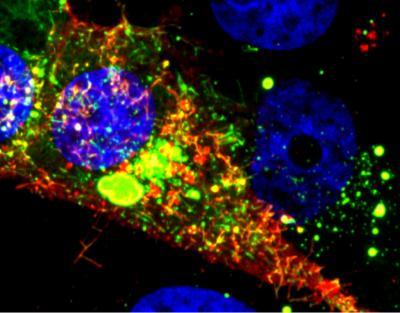
Image shows a cell infected with RSV. The RNA tagged by the probe is shown in red, while the nucleoprotein is green. Courtesy of Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo
The research team, which included scientists from Vanderbilt University and Emory University, used a probe technology that quickly attaches to RNA within cells. The probe uses multiple fluorophores to indicate the presence of the viral RNA, allowing the researchers to see where it goes in host cells – and to watch as infectious particles leave the cells to spread the infection.
"Being able to see the genome and the progeny RNA that comes from the genome with the probes we use really give us much more insight into the replication cycle," Santangelo said. "This gives us much more information about what the virus is really doing. If we can visualize the entry, assembly and replication of the virus, that would allow us to decide what to go after to fight the virus."
The research depended on a new method for labelling RNA viruses using multiply-labeled tetravalent RNA imaging probes (MTRIPS). The probes consist of a chimeric combination of DNA and RNA oligonucleotide labeled internally with fluorophores tetravelently complexed to neutravidin. The chimeric combination was used to help the probes evade cellular defenses.
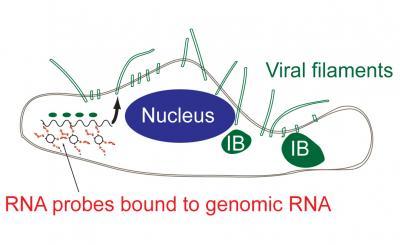
This diagram shows how the probe enters a cell to tag the viral RNA to provide information on replication. ourtesy of Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo
"There are lots of sensors in the cell that look for foreign RNA and foreign DNA, but to the cell, this probe doesn't look like anything," Santangelo explained. "The cell doesn't see the nucleic acid as foreign."
Introduced into cells, the probes quickly diffuse through a cell infected with RSV and bind to the virus's RNA. Though binding tightly, the probe doesn't affect the normal activities of the virus and allows researchers to follow the activity for days using standard microscopy techniques. The MTRIPS can be used to complement other probe technology, such as GFP and gold nanoparticles.
Work done by graduate student Eric Alonas to concentrate the virus was essential to the project, Santangelo said. The concentration had to be done without adversely affecting the infectivity of the virus, which would have impacted its ability to enter host cells.
"It took quite a bit of work to get the right techniques to concentrate the RSV," he said. "Now we can make lots of infectious virus that's labelled and can be stored so we can use it when we want to."
To study the infection's progress in individual cells, the researchers faced another challenge: living cells move around, and following them complicates the research. To address that movement, the laboratory of Thomas Barker – also in the Coulter Department – used micro-patterned fibronectin on glass to create 50-micron "islands" that contained the cells during the study.
Among the mysteries that the researchers would like to tackle is why certain lung cells are severely infected – while others appear to escape ill effects.
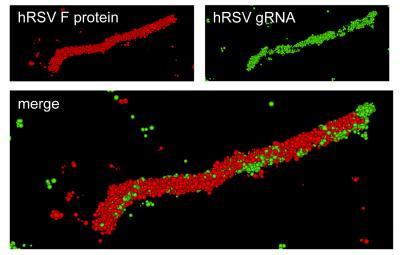
Super-resolution optical image of a specific hRSV viral filament produced with dSTORM technology. The viral filament is approximately 4 microns in length, typical of hRSV. Image courtesy of Eric Alonas and Philip Santangelo
"If you look at a field of cells, you see huge differences from cell to cell, and that is something that's not understood at all," Santangelo said. "If we can figure out why some cells are exploding with virus while others are not, perhaps we can figure out a way to help the bad ones look more like the good ones."
In addition to those already mentioned, the research team included James Crowe, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University; Elizabeth Wright, assistant professor in the School of Medicine at Emory University; Daryll Vanover, Jeenah Jung, Chiara Zurla, Jonathan Kirschman, Vincent Fiore, and Alison Douglas from the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University; Aaron Lifland and Manasa Gudheti from Vutara Inc. in Salt Lake City, and Hong Yi from the Emory University School of Medicine.
One of the challenges of studying RSV is maintaining its activity in the laboratory setting – a problem parents of young children don't share.
"When you handle this virus in the lab, you have to always be careful about it losing infectivity," Santangelo noted. "But if you take a room full of children who have not been infected and let one infected child into the room, 15 minutes later all of the children will be infected."
ACS Nano. Source: Georgia Institute of Technology





Comments